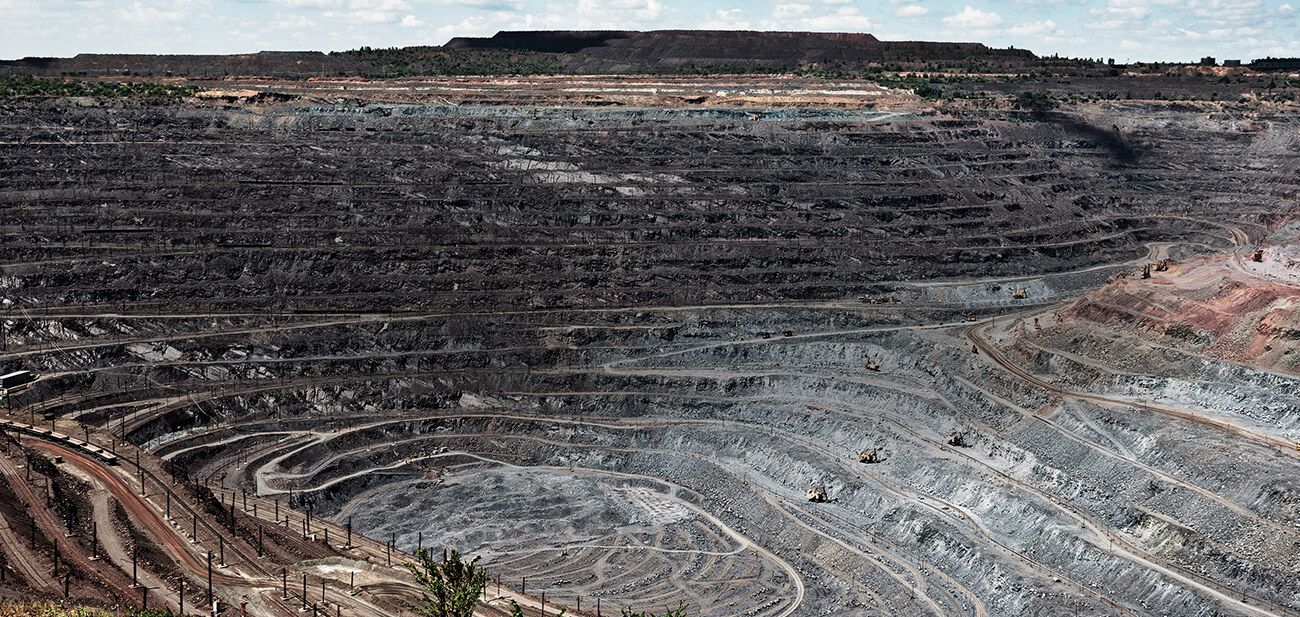

Leachate is a liquid pollutant that forms when water interacts with waste materials, carrying contaminants that seriously threaten water quality. At G3SoilWorks, we understand the importance of addressing this issue to protect our water resources and ecosystems. Without proper management, leachate can lead to long-term contamination of water supplies, with devastating effects on human health and the environment.
Leachate refers to the contaminated liquid that forms when water percolates through waste. This liquid, often rich in pollutants, can come from various sources such as leachate landfills, industrial waste sites, and agricultural runoff.
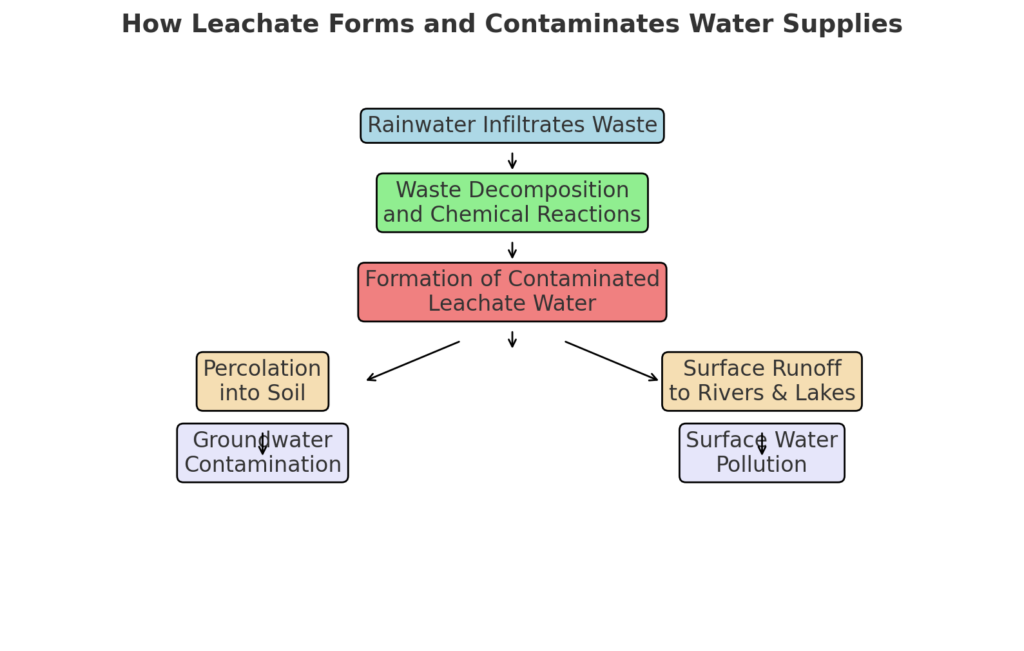
Leachate formation occurs when water interacts with waste materials, dissolving and transporting harmful substances. Common sources include:
A leachate landfill is one of the most significant sources of leachate. It forms as rainwater infiltrates landfills, dissolving various waste materials and accelerating the breakdown of organic matter. This process releases a complex mixture of hazardous pollutants into the liquid.
Landfill leachate poses unique challenges due to its diverse mix of contaminants, such as:
Leachate often infiltrates water resources through several pathways, threatening both groundwater and surface water:
The lack of containment in outdated or poorly managed systems exacerbates these risks.
The contamination of water resources is the most pressing environmental concern linked to leachate. Key problems include:
Leachate contains a wide range of harmful pollutants, including:
Heavy metals and pathogens in leachate pose significant threats to water quality and public health. Lead, mercury, and cadmium accumulate in aquatic systems, causing long-term contamination. When these metals seep into drinking water sources, they can lead to severe health problems, including organ damage, neurological disorders, and developmental issues in children. Pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites in leachate further exacerbate risks by contaminating water supplies, causing outbreaks of waterborne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and gastrointestinal infections. These pollutants not only degrade water quality but also pose chronic health risks to communities relying on untreated or poorly managed water sources.
Leachate contamination leads to severe environmental damage, including:
Leachate contamination also poses significant health concerns, such as:
Leachate management is a critical aspect of environmental protection, overseen by regulatory bodies such as the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and local water quality boards, which establish guidelines and standards for containment and treatment. Additionally, various companies and organizations specialize in leachate management, offering advanced technologies like bioreactors, reverse osmosis systems, and monitoring solutions. Collaborative efforts among governments, private enterprises, and environmental groups play a vital role in addressing the complex challenges posed by leachate to ensure sustainable waste management and water resource protection.
Effective management and treatment of leachate requires advanced technologies and practices:
Reducing leachate formation starts with sustainable waste management practices:
Managing leachate effectively starts with understanding the specific risks and implementing proactive measures. Here are practical steps communities and businesses can take to assess and mitigate leachate risks:
By taking these steps, communities and businesses can significantly reduce the environmental and health risks associated with leachate, ensuring a safer and cleaner future.

Leachate contamination is a critical issue that demands attention and action. At G3SoilWorks, we emphasize the importance of monitoring and managing leachates to protect water resources and ecosystems. By implementing advanced leachate systems, reducing waste, and improving treatment processes, we can mitigate the long-term risks posed by leachate water. Protecting water quality requires collective effort—let’s work together to ensure a safer, cleaner future. Call us at +1 714-668-5600 for more information.
1. Can leachate formation be affected by climate conditions?
A: Yes, climate conditions play a significant role in leachate formation. Regions with high rainfall experience more leachate production due to increased water infiltration in landfills and waste sites. Conversely, arid climates may have slower leachate formation but could still face contamination risks from concentrated pollutants.
2. What role does landfill design play in controlling leachate?
A: Landfill design is crucial in managing leachate. Features like impermeable liners, drainage layers, and leachate collection systems help prevent seepage into the environment. Modern landfills also include covers to minimize rainwater infiltration and advanced monitoring systems to detect leaks.
3. How does leachate impact agricultural practices?
A: Leachate contamination in water sources used for irrigation can harm crops and soil health. Pollutants such as heavy metals and nitrates can accumulate in the soil, reducing fertility and potentially entering the food chain, posing risks to human and animal health.
Follow, engage, learn. Stop by our blog to see what’s happening at G3SoilWorks.
G3Soilworks – a full service geotechnical/ engineering geologic consulting firm serving clients since 2009 and delivering expert solutions with our highly experienced team and specialized consultants.
G3SoilWorks
350 Fischer Avenue Costa Mesa, CA 92626
Tel. 714.668.5600
E. info@g3soilworks.com